https://www.wahmg.com/)">
Centrifuge Tubes
Centrifuge Tubes
Centrifuge tubes are essential tools in laboratory settings, playing a crucial role in various scientific experiments and procedures. These small, conical or cylindrical tubes are designed to hold samples while being subjected to high centrifugal forces, allowing for the separation of components based on their density. This function is fundamental in many fields, including biochemistry, molecular biology, and clinical diagnostics.
One of the primary uses of centrifuge tubes is the preparation and separation of biological samples. In biochemistry labs, researchers often use centrifuge tubes to isolate proteins, cells, or nucleic acids. For instance, after lysing cells, centrifuge tubes can separate cellular debris from the target proteins, allowing for further analysis. The ability to separate components efficiently has made these tubes indispensable for processes such as DNA extraction, where precise isolation of genetic material is critical.
Centrifuge tubes also find widespread application in the clinical setting. In blood testing, for example, blood samples are placed in these tubes and spun in a centrifuge to separate plasma, white blood cells, and red blood cells. This separation is vital for various diagnostic tests, including metabolic panels and blood typing. The clear demarcation of layers in the tube allows for easy extraction of the specific component needed without contamination from others.
centrifuge tube uses in laboratory
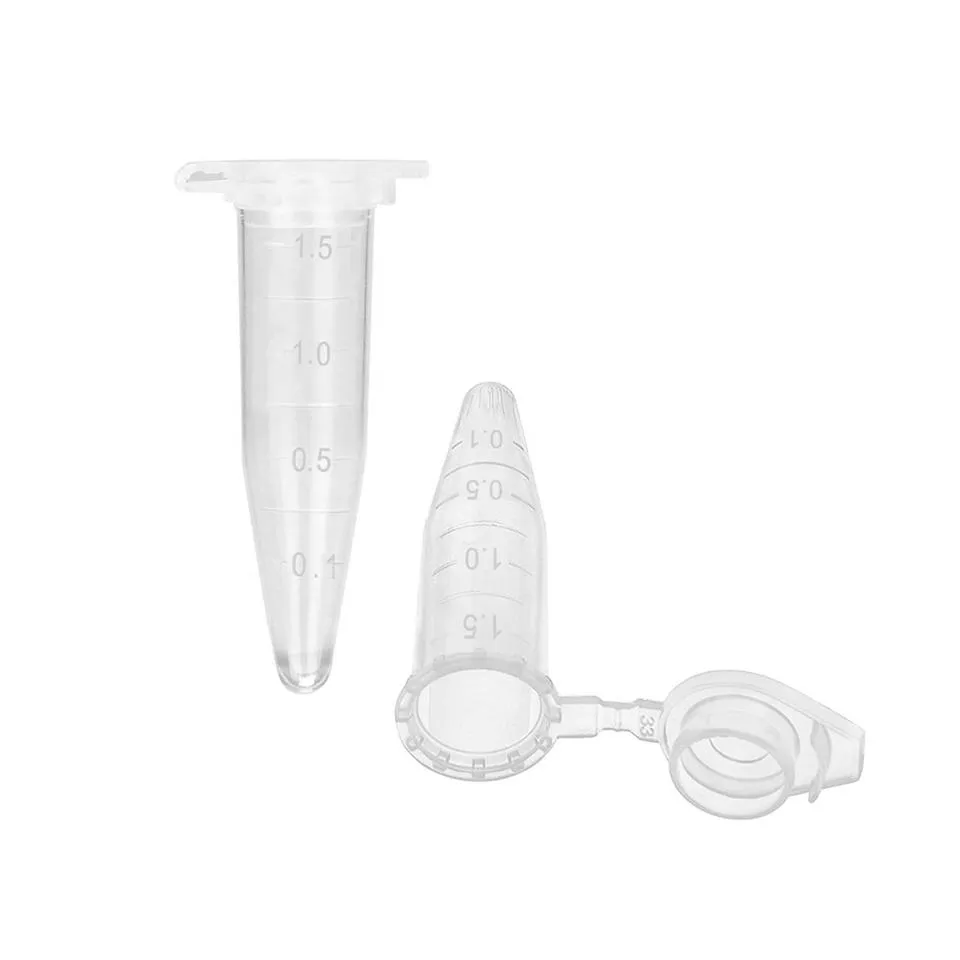
Moreover, the design of centrifuge tubes comes with various volume capacities, ranging from 1.5 mL to 50 mL, catering to the diverse needs of different experiments. They are typically made from high-quality plastic or glass, ensuring durability and resistance to the chemical properties of the samples. Many modern centrifuge tubes are also designed to be sterile, which is particularly important in sensitive biological applications, minimizing the risk of contamination and improving the reliability of results.
In addition to biological applications, centrifuge tubes are commonly used in environmental and material science laboratories
. For instance, in analyzing soil or water samples, researchers can use these tubes to separate suspended particles for further examination, such as determining the presence of pollutants or examining sediment composition.In summary, centrifuge tubes are versatile and invaluable instruments in laboratory settings. Their ability to effectively separate and isolate different components makes them essential for a wide array of applications, ranging from biological research to clinical diagnostics and environmental testing. As technology advances, the use and design of centrifuge tubes will likely continue to evolve, further enhancing their functionality and efficiency in scientific inquiry.
-
Wholesale Plastic Juice Bottles with Caps 16 oz Options Available Bulk Packaging SolutionsNewsJun.10,2025
-
Laboratory Apparatus Reagent Bottle – Durable & Chemical Resistant Bottles for Safe StorageNewsJun.10,2025
-
Squeezable Dropper Bottles Durable, Leak-Proof & CustomizableNewsMay.30,2025
-
Affordable Plastic Petri Plates Sterile & Disposable Lab-GradeNewsMay.30,2025
-
Eye Dropper Caps Precision 24/410 & Plastic Bottle-Compatible TipsNewsMay.30,2025
-
Affordable Mini Spray Bottle Price & Wholesale Deals Shop NowNewsMay.29,2025





















